CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THIS INFORMATION AS A PRINTABLE RESOURCE
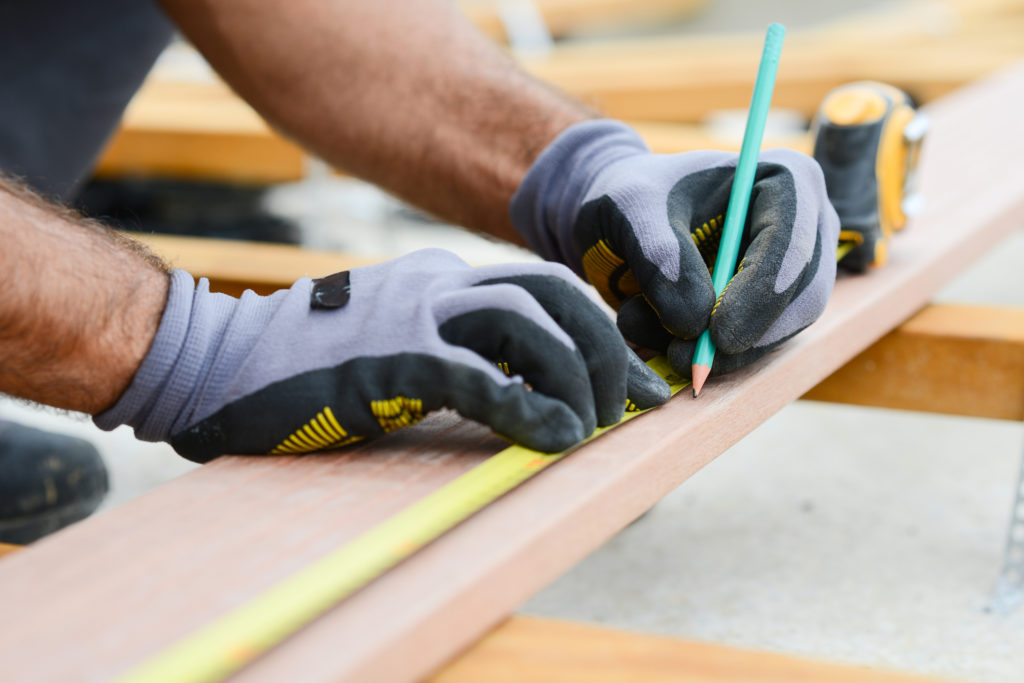
Most workplaces require hand protection by wearing gloves. Conduct a hazard assessment of the workplace to prevent hand/arm injuries. It’s important to consider the requirements of a particular application when choosing a glove material and as it relates to the hazards and protection.
Step 1: Identify Hazards
Step 2: Choose the Fabric
Step 3: Identify Level of Protection
Step 4: Training
Step 1: ARE YOUR WORKER’S WEARING THE CORRECT HAND-WEAR PPE?
Hazards to consider when deciding on the appropriate hand-wear PPE:
- Type of chemicals handled and the nature of the contact (total immersion, splash, etc.)
- Heat and cold exposure, sparks
- Sharp and rough objects
- Slippery, dirty objects (dry, wet, oily)
- Machines, guarding
- Pace of work
FACT: When recruiting or dispatching a worker to the job-site, ensure the safety hand-wear is worn to ensure safety while being productive.
STEP 2: CHOOSING THE FABRIC:
Cut-resistant gloves come in various fabrics, offering a different level of cut resistance:
1. Leather, Canvas or Metal Mesh Gloves – protection against cuts and burns. Leather or canvass gloves also protect against sustained heat.
2. Chemical- and Liquid-Resistant Gloves – protect against chemicals and are made with different kinds of rubber
HINT: the thicker the glove material, the greater the chemical resistance
3. Cotton Flannel Fabric and Coated Fabric Gloves – protection against dirt, slivers, chafing and abrasions. Coated gloves have plastic on one side offering slip-resistant qualities. These gloves are used for tasks ranging from handling bricks and wire to chemical laboratory containers.
STEP 3: Identify the Level Of Protection
ANSI standards are used across North America for puncture resistance, abrasion resistance and impact force.
Here’s an image showing the 9 ANSI cut levels and the types of hazards that they’re suitable for:

The 3 ANSI Forces:
ANSI/ISEA 138, for performance and classification for impact resistant hand protection to protect the knuckles and fingers from impact forces:
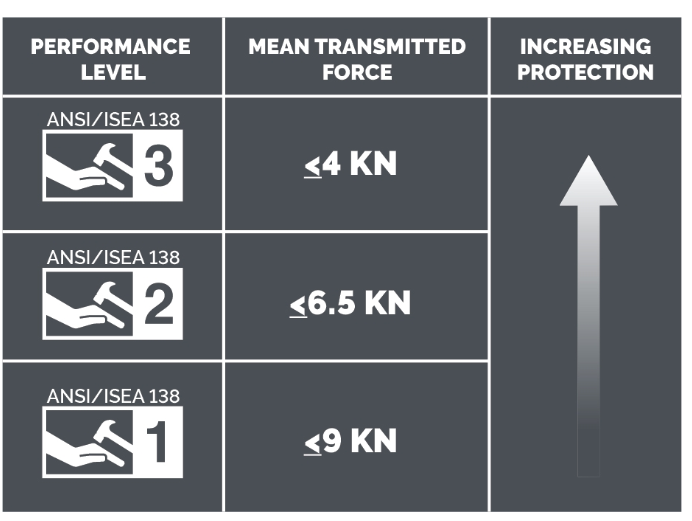
STEP 4: Training
Canadian standards also stress the employer’s responsibility to give relevant training to each worker who will use PPE. This training should cover when to wear specific types of PPE, how to properly use it, and what the limitations are.
This blog was written by:
Carla Villalta
ABL’s Occupational Wellness Manager
ABL Employment is a staffing agency specializing in filling general labour temporary jobs, including packaging jobs and warehouse jobs. Our ABL Careers division focuses on call centre and administrative positions. Contact us today to find the right staff for your needs!
You might also like:










